二分搜索
在本教程中,您将学习二分搜索排序的工作方式。 此外,您还将找到 C,C++ ,Java 和 Python 中的二分搜索的工作示例。
二分搜索是一种搜索算法,用于在排序数组中查找元素的位置。
在这种方法中,总是在数组的一部分中间搜索元素。
二分搜索只能在项目的排序列表上实现。 如果元素尚未排序,则需要首先对其进行排序。
二分搜索原理
二分搜索算法可以通过以下两种方式实现。
- 迭代方法
- 递归方法
递归方法遵循分治方法。
这两种方法的一般步骤将在下面讨论。
-
将在其中执行搜索的数组为:

初始数组
令
x = 4为要搜索的元素。 -
将两个指针分别在最低和最高位置设置为低和高。
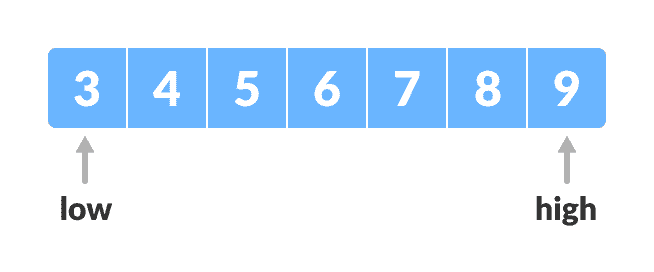
设置指针
-
找到数组中间的中间元素,即
(arr[low + high]) / 2 = 6。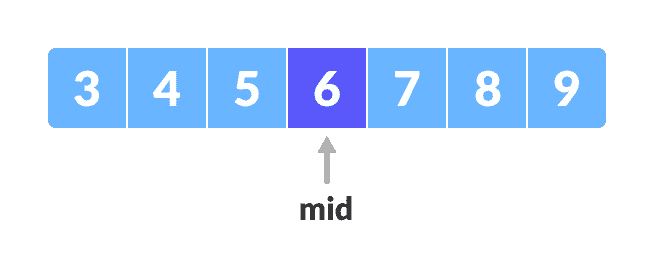
中间元素
-
如果
x == mid,则返回mid,否则将要搜索的元素与m进行比较。 -
如果为
x > mid,则将x与中间元素的右侧元素进行比较。 这是通过将low设置为low = mid + 1来实现的。 -
否则,将
x与中间元素的左侧元素进行比较。 这可以通过将high设置为high = mid - 1来完成。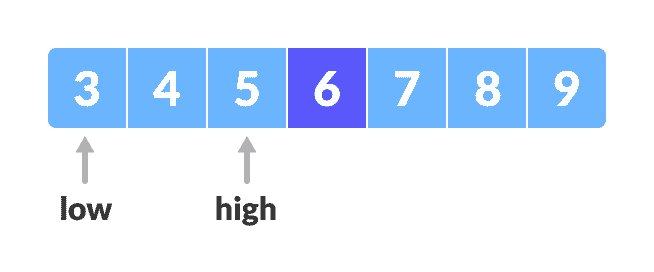
寻找中间元素
-
重复步骤 3 到 6,直到低点遇到高点为止。
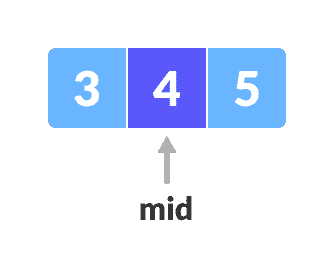
中间元素
-
找到
x = 4。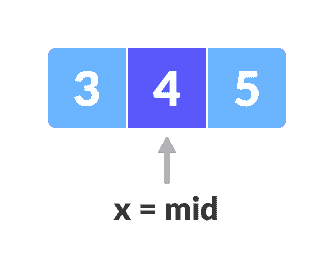
二分搜索算法
迭代方法
do until the pointers low and high meet each other.
mid = (low + high)/2
if (x == arr[mid])
return mid
else if (x > A[mid]) // x is on the right side
low = mid + 1
else // x is on the left side
high = mid - 1
递归方法
binarySearch(arr, x, low, high)
if low > high
return False
else
mid = (low + high) / 2
if x == arr[mid]
return mid
else if x < data[mid] // x is on the right side
return binarySearch(arr, x, mid + 1, high)
else // x is on the right side
return binarySearch(arr, x, low, mid - 1)
Python,Java,C/C++ 示例(迭代方法)
# Binary Search in python def binarySearch(array, x, low, high): # Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other while low <= high: mid = low + (high - low)//2 if array[mid] == x: return mid elif array[mid] < x: low = mid + 1 else: high = mid - 1 return -1 array = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] x = 4 result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array)-1) if result != -1: print("Element is present at index " + str(result)) else: print("Not found")
// Binary Search in Java
class BinarySearch {
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
// Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int array[] = { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int n = array.length;
int x = 4;
int result = ob.binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Not found");
else
System.out.println("Element found at index " + result);
}
}
// Binary Search in C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
// Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main(void) {
int array[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int x = 4;
int result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf("Element is found at index %d", result);
return 0;
}
// Binary Search in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
// Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (array[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main(void) {
int array[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int x = 4;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf("Element is found at index %d", result);
}
Python,Java,C/C++ 示例(递归方法)
# Binary Search in python def binarySearch(array, x, low, high): if high >= low: mid = low + (high - low)//2 # If found at mid, then return it if array[mid] == x: return mid # Search the left half elif array[mid] > x: return binarySearch(array, x, low, mid-1) # Search the right half else: return binarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high) else: return -1 array = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] x = 4 result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array)-1) if result != -1: print("Element is present at index " + str(result)) else: print("Not found")
// Binary Search in Java
class BinarySearch {
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If found at mid, then return it
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
// Search the left half
if (array[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(array, x, low, mid - 1);
// Search the right half
return binarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high);
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int array[] = { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int n = array.length;
int x = 4;
int result = ob.binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Not found");
else
System.out.println("Element found at index " + result);
}
}
// Binary Search in C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If found at mid, then return it
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
// Search the left half
if (array[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(array, x, low, mid - 1);
// Search the right half
return binarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high);
}
return -1;
}
int main(void) {
int array[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int x = 4;
int result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf("Element is found at index %d", result);
}
// Binary Search in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// If found at mid, then return it
if (array[mid] == x)
return mid;
// Search the left half
if (array[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(array, x, low, mid - 1);
// Search the right half
return binarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high);
}
return -1;
}
int main(void) {
int array[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int x = 4;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = binarySearch(array, x, 0, n - 1);
if (result == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf("Element is found at index %d", result);
}
二元搜索的复杂度
时间复杂度
- 最佳情况复杂度:
O(1) - 平均情况复杂度:
O(log n) - 最坏情况的复杂度:
O(log n)
空间复杂度
二分查找的空间复杂度为O(n)。
二分搜索应用
- 在 Java,.Net,C++ STL 库中
- 在调试时,二分搜索用于查明错误发生的位置。