Prim 算法
在本教程中,您将学习 Prim 的算法如何工作。 此外,您还将在 C,C++ ,Java 和 Python 中找到 Prim 算法的工作示例。
Prim 的算法是最小生成树算法,该算法将图作为输入并找到该图的边的子集,
- 形成包括每个顶点的树
- 在可以从图中形成的所有树中具有最小的权重总和
Prim 的算法如何工作
它属于称为贪婪算法的一类算法,该算法可以找到局部最优值,以期找到全局最优值。
我们从一个顶点开始,并不断添加权重最低的边,直到达到目标为止。
实现 Prim 算法的步骤如下:
- 使用随机选择的顶点初始化最小生成树。
- 找到将树连接到新顶点的所有边,找到最小值并将其添加到树中
- 继续重复步骤 2,直到得到最小的生成树
Prim 算法的示例
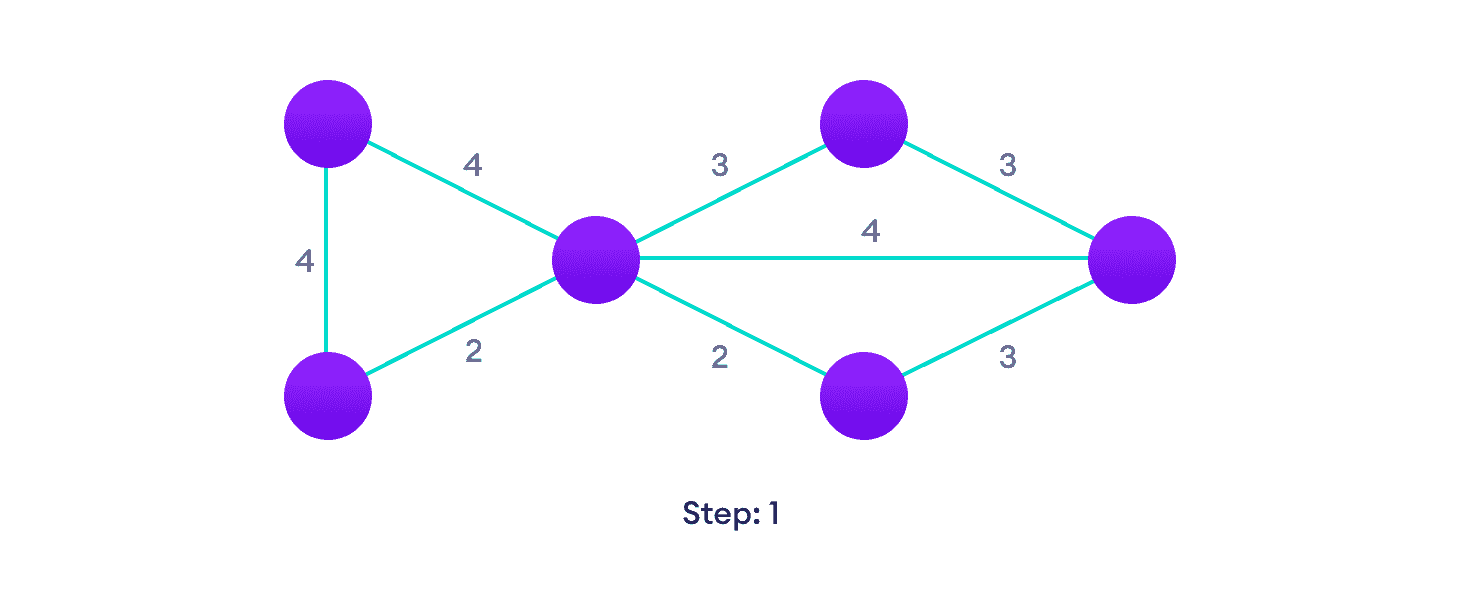
从加权图开始

选择一个顶点
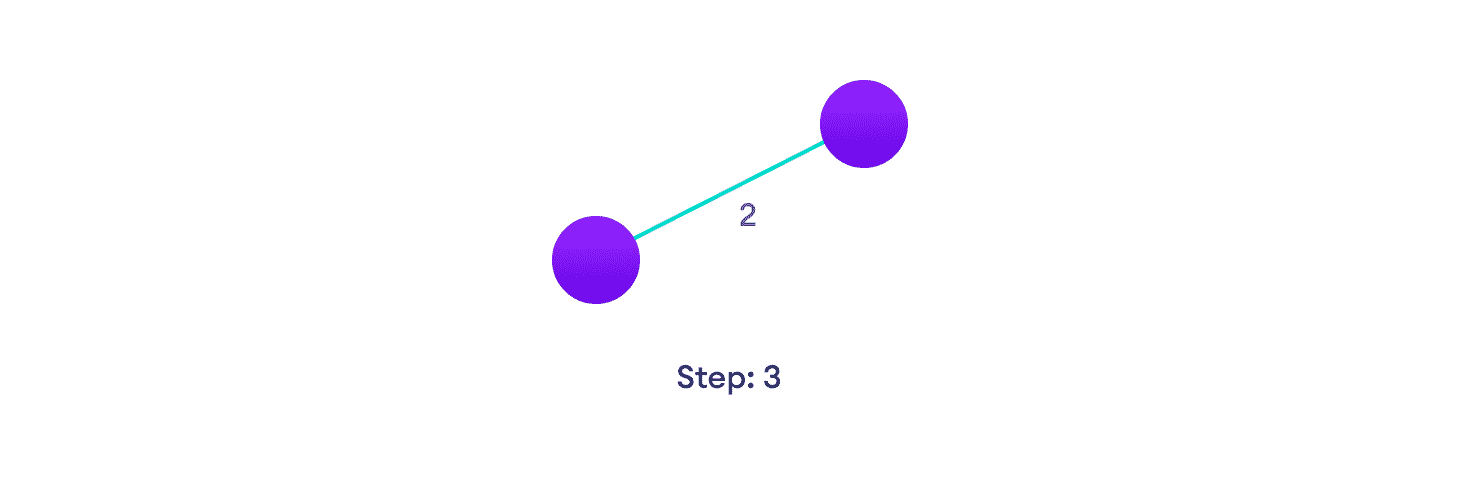
从该顶点选择最短边并添加
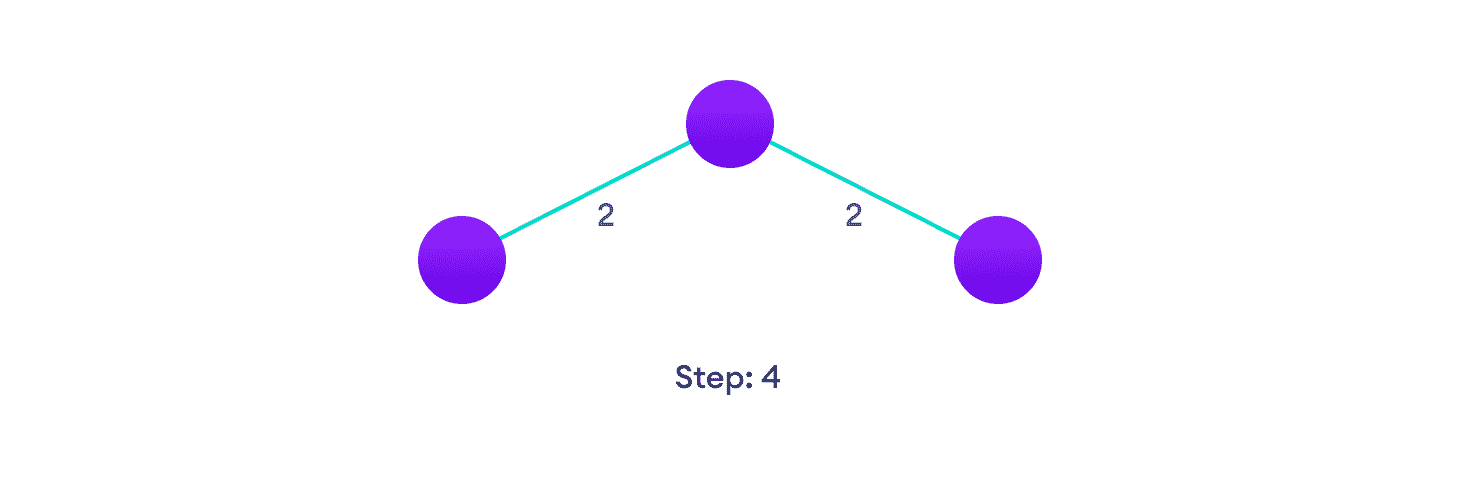
选择尚未在解决方案中的最近顶点
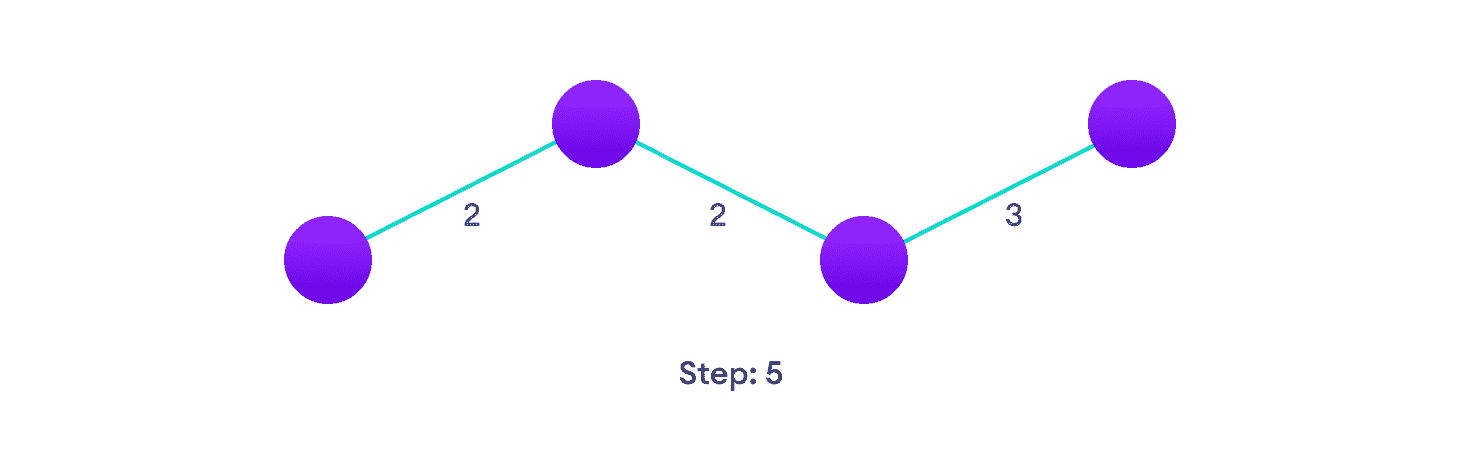
选择尚未出现在解决方案中的最近边,如果有多个选择,请随机选择一个
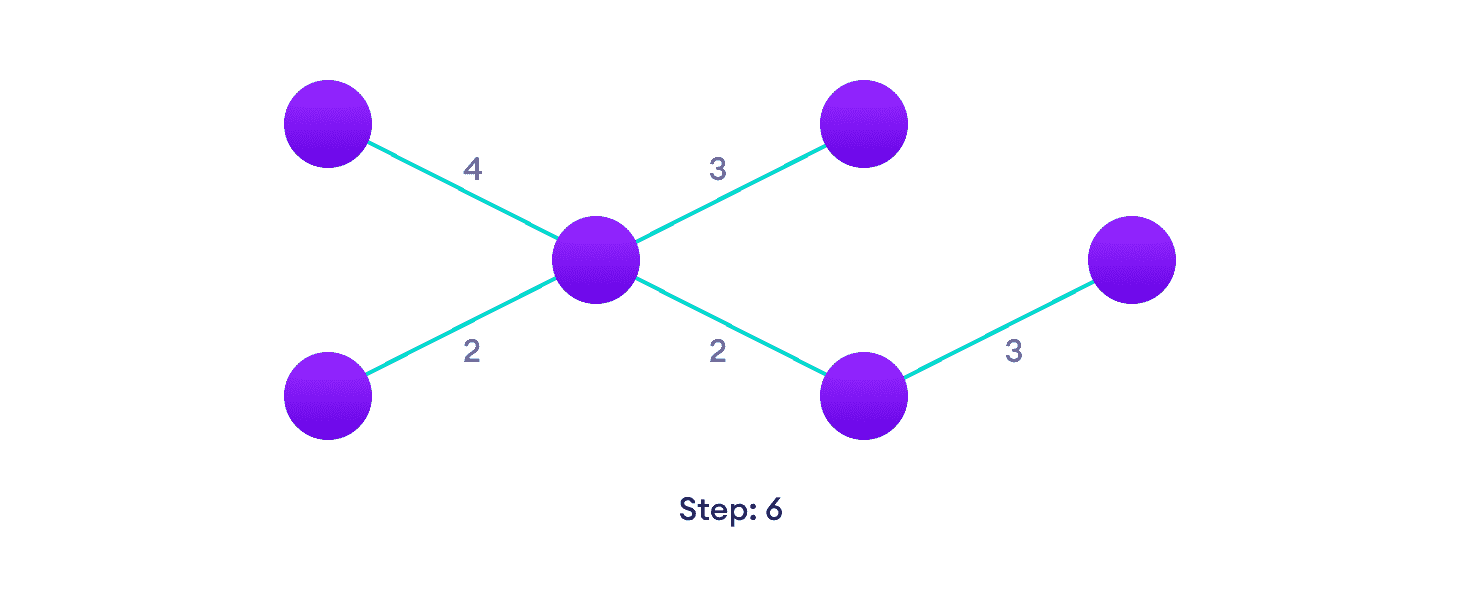
重复直到您有一棵生成树
Prim 算法伪代码
prim 算法的伪代码显示了我们如何创建两组顶点U和V-U。 U包含已访问的顶点列表,而V-U包含尚未访问的顶点列表。 通过连接最小权重边,将顶点从集合V-U移到集合U。
T = ∅;
U = { 1 };
while (U ≠ V)
let (u, v) be the lowest cost edge such that u ∈ U and v ∈ V - U;
T = T ∪ {(u, v)}
U = U ∪ {v}
Python,Java 和 C/C++ 示例
尽管使用图形的邻接矩阵表示,但是也可以使用邻接表来实现此算法,以提高效率。
# Prim's Algorithm in Python INF = 9999999 # number of vertices in graph V = 5 # create a 2d array of size 5x5 # for adjacency matrix to represent graph G = [[0, 9, 75, 0, 0], [9, 0, 95, 19, 42], [75, 95, 0, 51, 66], [0, 19, 51, 0, 31], [0, 42, 66, 31, 0]] # create a array to track selected vertex # selected will become true otherwise false selected = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0 # the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be # always less than(V - 1), where V is number of vertices in # graph # choose 0th vertex and make it true selected[0] = True # print for edge and weight print("Edge : Weight\n") while (no_edge < V - 1): # For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices #, calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. # if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise # choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. minimum = INF x = 0 y = 0 for i in range(V): if selected[i]: for j in range(V): if ((not selected[j]) and G[i][j]): # not in selected and there is an edge if minimum > G[i][j]: minimum = G[i][j] x = i y = j print(str(x) + "-" + str(y) + ":" + str(G[x][y])) selected[y] = True no_edge += 1
// Prim's Algorithm in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class PGraph {
public void Prim(int G[][], int V) {
int INF = 9999999;
int no_edge; // number of edge
// create a array to track selected vertex
// selected will become true otherwise false
boolean[] selected = new boolean[V];
// set selected false initially
Arrays.fill(selected, false);
// set number of edge to 0
no_edge = 0;
// the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be
// always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in
// graph
// choose 0th vertex and make it true
selected[0] = true;
// print for edge and weight
System.out.println("Edge : Weight");
while (no_edge < V - 1) {
// For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices
// , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1.
// if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise
// choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1.
int min = INF;
int x = 0; // row number
int y = 0; // col number
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (selected[i] == true) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
// not in selected and there is an edge
if (!selected[j] && G[i][j] != 0) {
if (min > G[i][j]) {
min = G[i][j];
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(x + " - " + y + " : " + G[x][y]);
selected[y] = true;
no_edge++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PGraph g = new PGraph();
// number of vertices in grapj
int V = 5;
// create a 2d array of size 5x5
// for adjacency matrix to represent graph
int[][] G = { { 0, 9, 75, 0, 0 }, { 9, 0, 95, 19, 42 }, { 75, 95, 0, 51, 66 }, { 0, 19, 51, 0, 31 },
{ 0, 42, 66, 31, 0 } };
g.Prim(G, V);
}
}
// Prim's Algorithm in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define INF 9999999
// number of vertices in graph
#define V 5
// create a 2d array of size 5x5
//for adjacency matrix to represent graph
int G[V][V] = {
{0, 9, 75, 0, 0},
{9, 0, 95, 19, 42},
{75, 95, 0, 51, 66},
{0, 19, 51, 0, 31},
{0, 42, 66, 31, 0}};
int main() {
int no_edge; // number of edge
// create a array to track selected vertex
// selected will become true otherwise false
int selected[V];
// set selected false initially
memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected));
// set number of edge to 0
no_edge = 0;
// the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be
// always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in
//graph
// choose 0th vertex and make it true
selected[0] = true;
int x; // row number
int y; // col number
// print for edge and weight
printf("Edge : Weight\n");
while (no_edge < V - 1) {
//For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices
// , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1.
// if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise
//choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1.
int min = INF;
x = 0;
y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (selected[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (!selected[j] && G[i][j]) { // not in selected and there is an edge
if (min > G[i][j]) {
min = G[i][j];
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%d - %d : %d\n", x, y, G[x][y]);
selected[y] = true;
no_edge++;
}
return 0;
}
// Prim's Algorithm in C++
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define INF 9999999
// number of vertices in grapj
#define V 5
// create a 2d array of size 5x5
//for adjacency matrix to represent graph
int G[V][V] = {
{0, 9, 75, 0, 0},
{9, 0, 95, 19, 42},
{75, 95, 0, 51, 66},
{0, 19, 51, 0, 31},
{0, 42, 66, 31, 0}};
int main() {
int no_edge; // number of edge
// create a array to track selected vertex
// selected will become true otherwise false
int selected[V];
// set selected false initially
memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected));
// set number of edge to 0
no_edge = 0;
// the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be
// always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in
//graph
// choose 0th vertex and make it true
selected[0] = true;
int x; // row number
int y; // col number
// print for edge and weight
cout << "Edge"
<< " : "
<< "Weight";
cout << endl;
while (no_edge < V - 1) {
//For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices
// , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1.
// if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise
//choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1.
int min = INF;
x = 0;
y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (selected[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (!selected[j] && G[i][j]) { // not in selected and there is an edge
if (min > G[i][j]) {
min = G[i][j];
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
}
}
cout << x << " - " << y << " : " << G[x][y];
cout << endl;
selected[y] = true;
no_edge++;
}
return 0;
}
Prim 与 Kruskal 算法
Kruskal 算法是另一种流行的最小生成树算法,它使用不同的逻辑来查找图的 MST。 Kruskal 算法不是从顶点开始,而是对所有边从低权重到高边进行排序,并不断添加最低边,而忽略那些会产生循环的边。
Prim 的算法复杂度
Prim 算法的时间复杂度为O(E log V)。
Prim 的算法应用
- 铺设电线电缆
- 在网络设计中
- 在网络周期内制定协议